The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) significantly impacts how businesses access and handle the personal information of California residents. For companies, understanding and complying with CCPA requirements is essential to avoid penalties and protect consumer data. This guide will outline the key steps and best practices for CCPA compliance, from data security to consumer rights management.
What is the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)?
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is a state-level data privacy law in the United States, which took effect on January 1, 2020. It grants California residents rights over their personal information, including the right to know what data is collected, the right to have their data deleted, and the right to opt out of the sale of their information to third parties.
Passed in 2018, the same year the GDPR came into effect, the CCPA was a response to growing concerns about data privacy and the practices of tech companies, particularly, regarding consumer information.
The California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) amended and expanded the CCPA, enhancing consumer privacy rights for the state’s residents, tightening requirements for businesses that collect and share personal information, and creating a new government agency to enforce California’s privacy laws.
The CPRA took effect on January 1, 2023, and enforcement began in February 2024 after a legal challenge delayed the original enforcement date of July 2023.
Learn the ins and outs of the CCPA
Understand everything you need to know about the CCPA, its associated rights, and how it affects California residents and businesses operating in the state
What’s the difference between the CCPA and the GDPR?
While both the CCPA (now known as the CPRA) and GDPR focus on protecting consumer privacy, there are key differences between the two. The GDPR applies to all EU residents, while the CCPA is specific to California residents.
One major distinction is in consent: GDPR requires consumers to opt in for data processing, while the CCPA uses an opt-out system for data sales. GDPR also grants broader rights, like the right to correct or limit the use of personal data.
Penalties differ as well. GDPR fines can reach up to 4% of global annual revenue, while CCPA penalties are set at specific amounts per violation. Additionally, the GDPR applies to any business handling EU resident data, whereas the CCPA has specific thresholds that determine which businesses are subject to the law.
If you’d like to learn more, explore our resource that highlights the key differences between the CCPA vs the GDPR.
Who needs to comply with the CCPA?
The CCPA has wide-reaching implications for businesses that handle personal information from California residents.
Essentially, any for-profit business that meets at least one of the compliance thresholds must comply with CCPA requirements. However, the CPRA amended and expanded the CCPA. Therefore, the below requirements reflect CPRA requirements:
- gross annual revenue of over USD 26,625,000
- buy, sell, or share the personal information of more than 100,000 consumers or households annually
- or those that earn at least 50% of their revenue from selling this data
The CCPA (now CPRA) applies to businesses operating in California, regardless of where they are headquartered. Therefore, even out-of-state companies with customers or business dealings in California must comply with CCPA compliance requirements.
Additionally, even organizations that don’t meet CCPA compliance thresholds, but still manage the personal information of California residents, should consider CCPA compliance, as data privacy requirements are only likely to expand in the future. This includes data processors that handle data on behalf of other businesses.
What are CCPA compliance requirements?
The CCPA strengthens consumer control over personal data and requires businesses to meet specific obligations. From securing data to providing clear notices, companies must follow several key requirements to stay compliant with the law.
CCPA data security requirements
The CCPA mandates that businesses implement and maintain reasonable security procedures and practices to protect consumers’ personal information. While the law does not specify exact security measures, it requires businesses to assess their data collection practices and implement appropriate safeguards.
These measures may include encryption of sensitive data, access controls, regular security audits, and employee training on data protection. Businesses should also have incident response plans in place to address potential data breaches. The law emphasizes the importance of preventing unauthorized access, destruction, use, modification, or disclosure of personal information.
CCPA notice requirements
To meet CCPA compliance requirements, businesses must provide clear and conspicuous notice to consumers about their data collection practices. This notice should be given at or before the point of data collection.
Using a website plugin or a CCPA compliance software, your cookie notice must inform consumers about the categories of personal information to be collected and the purposes for which it will be used. A cookie notice can be a separate document, or included as part of the privacy notice or policy, for example.
Additionally, businesses must inform consumers of their CCPA rights, including the right to access their personal information, request its deletion, and opt out of its sale. The notice should also include instructions on how consumers can exercise these rights and provide contact information for submitting requests.
CCPA cookie consent requirements
When it comes to the CCPA and cookies, the regulation does not explicitly require opt-in consent for cookies, it does consider certain types of cookie data as personal information. Businesses must disclose their use of tracking cookies and similar technologies in their privacy policies. They should explain what information is collected through cookies, how it is used, and whether it is shared with or sold to third parties.
If the information collected through Google cookies or other types of tracking technologies is sold or shared, businesses must provide a clear and conspicuous “Do Not Sell Or Share My Personal Information” link on their website (“Or Share” was added when the CPRA came into effect). This enables consumers to opt out of the sale of their personal information, including data collected through cookies.
Are you aware of all the cookies in use on your website?
Use our speedy cookie audit tool to check cookies on your website and generate a detailed cookie audit report in minutes.
CCPA opt-out requirements
Compliance with the CCPA means consumers have the right to opt out of the sale of their personal information. Businesses that sell personal information must provide a clear and conspicuous “Do Not Sell My Personal Information” link on their homepage and in their privacy policy. This link should direct people to a page where they can easily exercise their right to opt out, often managed through CCPA compliance software.
Businesses must honor opt-out requests and refrain from selling the personal information of consumers who have opted out. They are also prohibited from requesting authorization to sell personal information for at least 12 months after an individual has opted out.
CCPA privacy policy requirements
CCPA website compliance requires businesses to update their privacy policies to include specific information about their data practices and consumer rights. This process can be streamlined with CCPA compliance software, ensuring that all necessary disclosures are made. The privacy policy must disclose:
- categories of personal information collected in the past 12 months
- sources from which personal information is collected
- purposes for processing personal information
- categories of third parties with whom personal information is shared, if any
- specific pieces of personal information collected about consumers
- consumer rights under CCPA and how to exercise them
- controller contact information, including methods for submitting consumer requests
- process for verifying consumer requests
The privacy policy should be easily accessible, written in clear and straightforward language, and updated at least once every 12 months.
Instantly generate your CCPA-compliant privacy policy
Craft a personalized privacy policy for your website that aligns with the CCPA in just a few easy steps.
CCPA compliance training requirements
To meet CCPA training requirements, companies need to ensure their employees are well-trained in handling personal data. This training should cover key areas, like recognizing protected data, managing consumer requests for data access or deletion, and understanding the CCPA’s consumer rights. Employees who work in data processing or customer service should know how to respond to privacy requests accurately and in a timely manner and help maintain security standards.
In addition, regular updates to your company’s training materials are essential, especially when laws, technologies in use, or company policies change. This helps ensure that your staff stays informed and prepared to follow best practices.
CCPA compliance checklist
The CCPA aims to strengthen consumer privacy rights and set clear responsibilities for businesses that manage the personal information of California residents. Therefore, it’s recommended that companies follow these CCPA compliance guidelines to meet legal requirements and build trust with customers.
1. Identify and classify data
Conduct thorough and regular audits of all the personal information your business collects and uses, including names, addresses, and browsing history. Understand where this data comes from, how it’s used, and who has access to it. This helps you comply with the CCPA and improve security measures.
2. Update your company’s privacy policy
Your privacy policy should be clear, detailed, and up-to-date. It must explain what personal data you collect, why you collect it, and the rights consumers have under the CCPA. Make sure the policy is easy to find and understand. Doing so provides transparency to your customers.
3. Set up processes for consumer data requests
Create systems, such as an online portal or phone line, that enable consumers to exercise their CCPA rights. These include the right to access, delete, or opt out of the sale of their personal information. Make sure you verify consumer identities and respond to requests within 45 days.
4. Commit to data security
Put in place reasonable security measures (or best practices, ideally) to protect personal information from unauthorized access, loss, damage, or other data breaches. Measures can include encryption, regular security audits, and a response plan in case of a breach is also a requirement. The CCPA security requirements that you implement across your company should match the sensitivity of the data you handle.
5. Protect minors’ data
If your business collects data from minors, you must obtain opt-in consent from consumers aged 13 to 16 directly, and parental consent for those under age 13, as required by the CCPA. Additionally, if your business targets children under age 13, you must comply with the Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA), which imposes stricter guidelines for collecting and handling children’s data.
6. Manage vendors and service providers
Review your agreements with third-party vendors for CCPA compliance when handling personal information. Contracts should clearly outline how they will protect data and meet security standards, among other stipulations.
7. Train employees on CCPA compliance
Regularly train and refresh your employees on CCPA requirements as laws, technologies, and operations change. Especially those managing personal data or responding to consumer requests. Effective training fosters a strong privacy culture and helps enable compliance across the organization.
8. Maintain accurate and detailed records
Maintain detailed records of all consumer data requests and your responses for at least 24 months. This documentation is essential for demonstrating compliance if your business faces an audit or regulatory inquiry.
CCPA compliance for small businesses
While the CCPA mainly targets larger businesses, small companies can still benefit from voluntarily adopting CCPA-like practices. Doing so can help build trust with customers and prepare for future regulations.
If you’re a small business seeking to meet CCPA compliance requirements, start by mapping out how you collect and use data. Then update your privacy policies to clearly explain your data practices and consumer rights. It’s also important to implement basic data security measures.
Even if not legally required, creating straightforward processes for handling consumer requests can strengthen customer relationships. Regular staff training on best practices for data handling is a smart move for businesses of any size.
Who enforces the CCPA?
Since the CCPA’s start, the Attorney General’s Office has led enforcement by investigating potential violations, ensuring businesses follow the law, and prioritizing consumer privacy. Their efforts focus on proper data handling, upholding consumer rights, and maintaining transparency in privacy policies, helping to create a solid framework for protecting privacy in California.
What are CCPA penalties for violating compliance requirements?
Under the CCPA, businesses face significant penalties for failing to comply with its requirements. For unintentional violations, the fines can reach up to USD 2,663 per incident. If a violation is intentional or repeated, the penalties can be as high as USD 7,988 per incident. Each affected consumer is treated as a separate violation, so fines can add up quickly.
In the event of a data breach, consumers can seek damages ranging from USD 107 to USD 799 per incident. When determining penalties, enforcement authorities consider factors like how severe the violation was, whether it was intentional, and the organization’s prior compliance record.
How Cookiebot CMP can help you meet CCPA compliance requirements
Achieving CCPA compliance may sound complex, but it doesn’t have to be. Cookiebot CMP is a CCPA compliance solution. Our tool can help you by automatically scanning your website to identify all cookies and tracking technologies in use. This list can then populate your consent banner and cookie notice. Present your website visitors with an accurate cookie banner with comprehensive information, which helps you comply with the CCPA, among other global privacy laws.
Also, under the CCPA, businesses must enable California residents to opt out of the sale of their personal information, disclose what data has been collected, and delete it upon request. Cookiebot CMP helps you meet these requirements by detecting if a user is from California and displaying a “Do Not Sell My Personal Information” link in the cookie declaration, as required by the CCPA. It then keeps a detailed record of each person’s choices over time for auditing purposes.
This is what the Cookiebot CMP CCPA cookie compliance solution looks like for your end users:
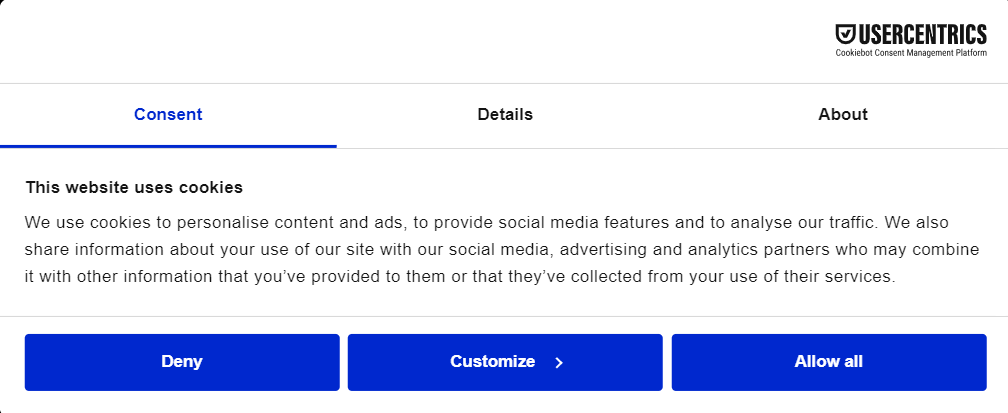
Experience it for yourself and try Cookiebot CMP for 14 days – free of charge! No credit card required.
FAQ
CCPA compliance refers to adhering to the requirements set forth by the California Consumer Privacy Act, which aims to enhance privacy rights and consumer protection for California residents.
CCPA compliance requires transparency about data collection, enabling access, deletion, and opt-out of personal information sales, and implementing security measures. Businesses must update privacy policies, handle consumer requests, manage vendors, and train employees.
To meet CCPA compliance requirements, businesses must take steps to protect the personal data of California residents and respect their privacy rights. This includes enabling consumers to opt out of data collection and sales. Key actions involve creating a data inventory and auditing it and data operations regularly, updating privacy policies, setting up procedures for handling consumer requests, and ensuring robust data security measures are in place.
Common CCPA compliance solutions include Cookiebot CMP, which provides a consent management platform to help businesses manage user consent and comply with various data privacy regulations, such as the CCPA.
CCPA service provider contracts must ensure that personal information is only used for the agreed business purposes. They should also require the provider to follow CCPA rules, assist with consumer requests, and implement proper security measures.
CCPA DSAR requirements mandate that businesses respond to verified consumer requests for access to their personal information within 45 days, with a possible 45-day extension if necessary. Businesses must provide consumers with the specific personal information collected, the categories of sources and third parties the information is shared with, and the purpose for collecting or selling the data. Individuals can also request deletion of their data.